Advanced Cane Sugar Processing: Enhancing Efficiency and Sustainability
Advanced Cane Sugar Processing: Enhancing Efficiency and Sustainability
Blog Article
An In-Depth Overview to the Environmental Impact and Sustainability Practices in Walking Stick Sugar Handling
The environmental influence of cane sugar processing offers a complex selection of obstacles that warrant cautious examination. From dirt deterioration and excessive water usage to the carbon impact connected with farming and production, the effects of conventional methods are far-ranging. In contrast, the adoption of ingenious sustainability steps supplies a pathway towards a lot more accountable manufacturing approaches. Recognizing the interaction between these problems is essential for stakeholders in the industry. What details methods can be executed to strike a balance in between efficiency and environmental stewardship? The responses exist in a closer consider both the obstacles and prospective options.
Review of Cane Sugar Handling
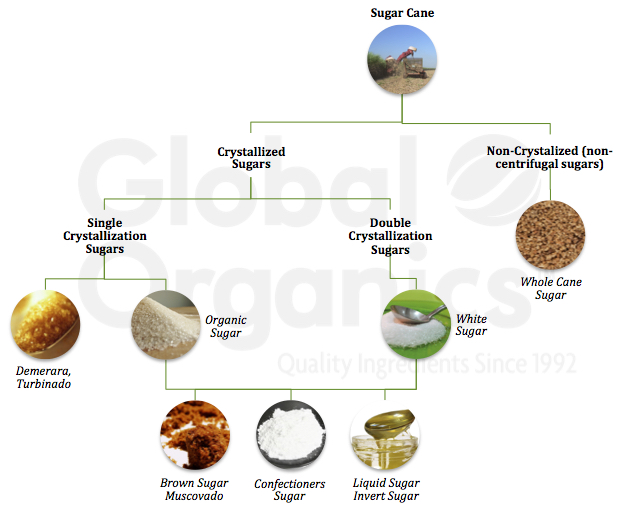
Walking stick sugar handling involves a series of methodical steps that change sugarcane into refined sugar. Initially, collected sugarcane is delivered to processing facilities, where it goes through cleaning to eliminate soil and debris. Following this, the walking cane is crushed to remove juice, which is after that cleared up by eliminating pollutants via home heating and the enhancement of lime.
The cleared up juice undergoes evaporation, where water is gotten rid of to focus the sugar web content. These crystals are separated from the continuing to be syrup using centrifugation, resulting in raw sugar.
The end product is then dried and packaged for distribution. Throughout this entire procedure, preserving performance and quality assurance is necessary to make certain the sugar fulfills market requirements. Each action in walking cane sugar handling not only adds to the end product but likewise has ramifications for source use and waste generation, setting the phase for conversations on sustainability and ecological influences related to sugar manufacturing.
Ecological Challenges of Production
The production of walking cane sugar presents several considerable environmental difficulties that warrant interest. One key problem is the considerable usage of agrochemicals, consisting of chemicals and plant foods, which can bring about soil deterioration, biodiversity loss, and contamination of neighborhood water sources. The drainage from sugarcane areas typically carries these chemicals right into neighboring communities, interrupting aquatic life and impacting the health of areas reliant on these water bodies.
Another challenge is the high energy consumption connected with sugarcane handling. The boiling and refining phases require substantial warmth, primarily produced by burning fossil fuels, adding to greenhouse gas exhausts. Furthermore, the expansive land area required for sugarcane growing can result in logging and habitat devastation, further exacerbating climate change and threatening wild animals.
In addition, the labor practices in some areas elevate moral issues, as workers might encounter inadequate working problems and inadequate incomes. This circumstance frequently perpetuates a cycle of hardship in neighborhood communities. Cane Sugar Processing. Attending to these ecological challenges is essential for developing a lot more lasting techniques in walking cane sugar manufacturing, inevitably benefiting both the setting and the communities associated with this sector
Water and Land Use Influence
Water resources and land utilization are important components in the cane sugar market that substantially affect the setting. The farming of sugarcane requires substantial water input, with price quotes suggesting that it can consume up to 2,000 liters of water per kg of sugar produced. This intensive use water usually causes depletion of neighborhood water resources, impacting not only the sugarcane plantations but also surrounding ecosystems and areas that depend on the same water resources for agriculture and domestic use.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-cane-sugar-5200549-hero-02-b1985b1d539645fb9a038b9c3e73f681.jpg)
Additionally, land usage for sugarcane growing can lead to logging and the conversion of all-natural environments into monoculture haciendas. This method lessens biodiversity, interrupts neighborhood ecosystems, and adds to dirt deterioration. The development of sugarcane areas typically intrudes on important agricultural land, producing competition for sources in between food and biofuel production.
Sustainable methods, such as optimizing watering strategies and implementing plant turning, are important to alleviate these effects. By embracing more reliable water usage and land administration techniques, the walking stick sugar market can minimize its environmental footprint, ensuring an equilibrium between farming productivity and ecological preservation.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas exhausts represent a significant ecological issue within the walking cane sugar handling industry, particularly as agricultural practices expand to fulfill worldwide demand. The farming of sugarcane, a crop that prospers in exotic climates, depends greatly on artificial fertilizers and pesticides, which contribute to laughing gas emissions. Additionally, land-use adjustments, consisting of logging for brand-new sugarcane haciendas, release carbon dioxide stored in plant life and soil.
Throughout handling, power consumption is another significant resource of greenhouse gas exhausts - Cane Sugar Processing. Lots of sugar mills utilize nonrenewable fuel sources to power machinery and produce heat, causing considerable carbon footprints. Additionally, the transportation of raw sugarcane and ended up products includes layers of discharges through gas combustion in cars
The cumulative impact of these discharges aggravates environment change, posturing dangers not only to the environment but also to the long-lasting viability of the market. Stakeholders should recognize the immediate need for extensive techniques that deal with these discharges. This involves evaluating present farming methods, processing approaches, and transportation systems to determine locations for renovation and reduction. Attending to greenhouse gas emissions is essential for cultivating an extra lasting walking published here cane sugar market in a changing climate.
Sustainable Practices and Innovations
Sustainable methods and developments are significantly important in the walking cane sugar processing industry as stakeholders look for to lower environmental impacts while preserving productivity. One considerable development is the execution of incorporated crop monitoring, which maximizes resource use by combining soil administration, More about the author insect control, and plant rotation techniques. This approach enhances return while minimizing chemical inputs and protecting soil wellness.
In addition, the fostering of renewable resource sources, such as biomass from sugarcane deposits, has actually gained traction - Cane Sugar Processing. By converting waste products into energy, refining centers can decrease their dependence on nonrenewable fuel sources, thus decreasing greenhouse gas emissions
Water administration practices have actually likewise seen improvements via the recycling and reusing of water in processing plants, significantly minimizing freshwater consumption. Advancements in modern technology, such as precision agriculture, make it possible for farmers to keep track of plant wellness and source use better, making sure sustainable growing techniques.
Moreover, qualification programs like Fair Trade and Rain forest Partnership motivate environmentally accountable farming practices and advertise social equity within the supply chain. By embracing these lasting methods and advancements, the walking cane sugar processing sector can enhance its resilience and contribute positively to environmental stewardship.
Verdict
The environmental effect of walking stick sugar processing provides substantial obstacles, including dirt degradation, high water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions, together with honest issues related to labor practices. Addressing these issues with lasting techniques, such as incorporated plant monitoring, renewable power fostering, and water recycling, is vital. By advertising ecologically accountable and socially fair approaches in sugar manufacturing, the market can alleviate its unfavorable impacts, making certain a more sustainable future for both environments and communities included in this sector.
Walking stick sugar handling includes a collection of methodical steps that change sugarcane right into refined sugar. Each action in walking stick sugar handling not only contributes to the final product but also has implications for source use and waste generation, establishing the stage for discussions on sustainability and ecological influences connected with sugar production.
Greenhouse gas exhausts stand for a considerable ecological problem within the walking important site cane sugar handling market, particularly as farming practices broaden to satisfy international need.Lasting practices and developments are progressively crucial in the walking stick sugar processing market as stakeholders seek to decrease environmental impacts while keeping productivity.The ecological impact of cane sugar processing presents substantial challenges, consisting of dirt destruction, high water usage, and greenhouse gas emissions, alongside ethical issues connected to labor practices.
Report this page